RPO: The Clock That Defines Your Business Resilience
In the rapidly evolving landscape of enterprise technology, we often encounter a striking paradox. We meet organizations every week where the "Traditional IT" infrastructure is held to incredibly high standards of resilience, while the "Modern IT" side—where the company’s future growth and innovation reside—operates on shaky Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and fragmented Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs).
This disparity poses a significant risk. Why should the systems driving your future revenue be less resilient than the systems maintaining your legacy operations?
Before we dissect the chaos of modern data protection, let's establish the fundamental metric that governs resilience: RPO.
What is RPO? The Business Cost of Time
Imagine your company’s entire digital infrastructure suddenly vanishes. A server failure, a sophisticated cyberattack, or a simple human error wipes the slate clean. As your teams scramble to restore backups, one critical question determines the fate of your company: How much data are we willing to lose?
In the world of disaster recovery, the answer is your Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
Simply put, RPO is a measure of time that translates directly into business loss. It defines the maximum age of files that must be recovered from backup storage for normal operations to resume.
If your RPO is 24 hours, you are accepting that in a disaster, you will lose a full day of orders, transactions, and work.
If your RPO is 4 hours, you are limiting that loss to a half-day working day window.
The Executive Perspective:
For the CIO: RPO is an architectural blueprint. It dictates the rigorous backup schedules, the bandwidth requirements, and the storage infrastructure needed to capture data frequently enough to meet the objective.
For the CEO: RPO is a strategic "Pain Tolerance" metric. It is the threshold where data loss transitions from a manageable operational hiccup to a catastrophic failure that erodes brand trust and revenue.
The Traditional IT Success Story: A Legacy of Robust Protection
For decades, enterprises have poured investment into robust, near-zero data loss solutions for traditional workloads (physical servers and virtual machines). Organizations have spent millions on "Gartner Leader" products to ensure their foundational databases (like Oracle or SQL) and operating systems are bulletproof.
In this traditional domain, resilience is mature and well-understood:
Continuous Data Protection: We see solutions that back up entire environments daily, often supplemented by transaction log backups every 15 minutes.
Real-Time Granularity: Critical databases often feature "point-in-time" recovery, allowing administrators to roll back to a specific second in time over the last 30 to 90 days.
The "Clean Room" Investment: Companies are currently investing heavily in "Clean Room" environments—isolated, sterile recovery zones where data can be scanned for malware before being restored. This is a massive capital expenditure designed to ensure that when you restore a VM, you aren't re-infecting your network.
This level of investment is correct and necessary. No C-suite executive wants to face the board or the press to explain that the business has halted because basic infrastructure wasn't protected.
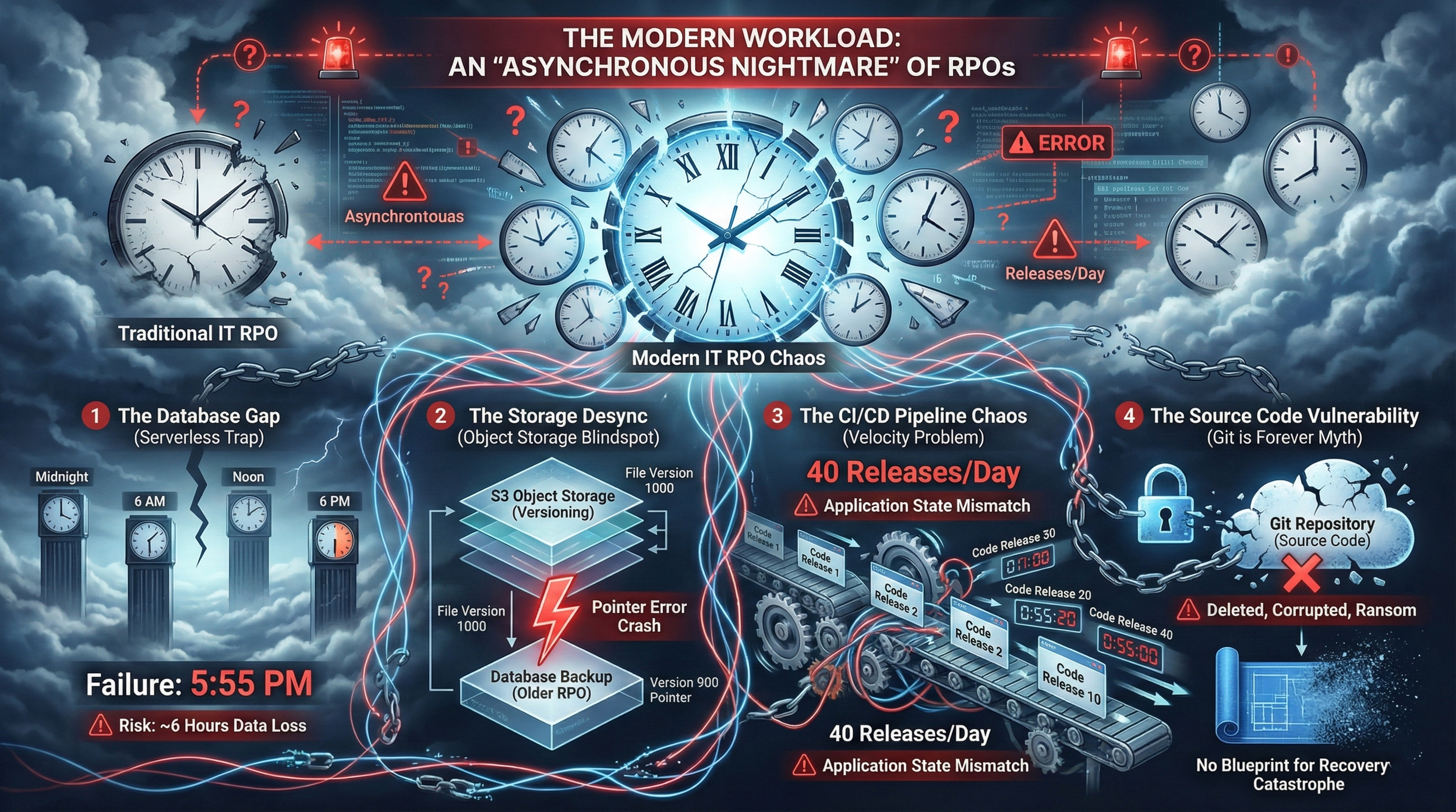
The Modern Workload: An "Asynchronous Nightmare"
However, when we shift focus to Modern Application solutions running on Kubernetes, that mature safety net vanishes. We enter a world of "microservices" where the application is split into dozens of small pieces, often managed by different tools with different schedules. This creates a "chaos of RPOs."
In Traditional IT, you backup the whole server. In Modern IT, you have to coordinate three distinct, moving targets:
You have multiple tools that keep different RPOs and the chance to match is minimum
1. The Database Gap (The "Serverless" Trap)
Modern apps often utilize "Serverless" or "No-Admin" databases managed by cloud providers or DevOps teams rather than dedicated DBAs. Because these aren't traditional servers, they often fall out of the central backup policy. They might be backed up only 4 times a day (Midnight, 6 AM, Noon, 6 PM).
The Risk: If a failure happens at 5:55 PM, you lose nearly 6 hours of customer data.
2. The Storage Desync (The Object Storage Blindspot)
Files, images, and documents are often stored in S3-compatible Object Storage. Here, teams rely on "Versioning"—a feature that keeps every change made to a file.
The Risk: While versioning is powerful, it is distinct from your database backup. You might have version 1,000 of a file, but if your database thinks you are on version 900 because it was restored from an older backup, your application will crash due to a "pointer error."
3. The CI/CD Pipeline Chaos (The Velocity Problem)
Then there is the code itself. A high-performing DevOps team might push 40 releases a day via their CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline. Each release changes the state of the application.
4. The Source Code Vulnerability (The "Git is Forever" Myth)
Many companies operate under the dangerous assumption that their code repositories are immutable and immune to deletion or infiltration. Consequently, they often fail to back up the actual source code, relying entirely on Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) workflows to rebuild their environments. The Risk: What happens if your Git repository is deleted, corrupted, or held for ransom? If the repository vanishes, your "blueprint" for recovery is gone. You end up in a catastrophe where rebuilding your environment is impossible because the instructions for doing so no longer exist.
The Ticking Time Bomb:
Imagine a developer pushes a code update at 10:00 AM that alters the database schema (the structure of how data is organized).
The code is "bad" or corrupts the data structure.
The DevOps team tries to revert the code. This takes minutes.
The Problem: The database is now "poisoned" by the new structure. You cannot just revert the code; you must also roll back the database.
The Disaster: Your last database backup was at 6:00 AM. You have to roll back the database 4 hours, losing all customer data created between 6:00 AM and 10:00 AM, just to fix a code error.
You have three different clocks (Code, Data, Database) ticking at different speeds. When they fall out of sync, the result is chaos.
Old picture created by Scott Adams where he make fun of a Companies Disaster Recovery Strategy
Solving the Puzzle with IssProtect for DevOps
Why are we protecting a modern, agile vessel with an old, heavy anchor? IssProtect for DevOps, powered by Veeam Kasten, introduces a new paradigm that bridges the gap between the "Agile Horses" of DevOps and the "Safety First" mandates of the CxO.
1. Application-Centric Protection (The Holistic View)
Veeam Kasten moves beyond the concept of "servers." It views the Application as the atomic unit of protection. It automatically discovers every component associated with a Kubernetes namespace—the code, the configurations, the secrets, the S3 object storage, and the databases.
The Benefit: When you take a backup, you aren't grabbing isolated puzzle pieces; you are capturing the entire finished picture.
2. Backup-As-Code: The New Era of Protection
Just as "Dissimilar Hardware Restore" revolutionized traditional backup by allowing Windows to be restored to any server, Backup-As-Code is the revolution for Modern IT.
Instead of treating backup as a separate "administrative task" scheduled by a calendar, we treat backup as lines of codes within the software delivery process.
The Mechanism: We integrate data protection instructions directly into the application's definition. The backup policy lives with the application, ensuring that as the app scales, its protection scales automatically.
3. The "Pre-Release Snapshot" & Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
This is where we solve the "Clean Room" cost dilemma. In traditional IT, you pay for a Clean Room to verify data. In Modern IT, Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows us to spin up a fresh, clean environment in minutes, test the data, and tear it down.
We integrate this into the CI/CD pipeline:
The Process: Before the "Deploy to Production" step, the pipeline triggers a Synchronized Snapshot via IssProtect.
The Result: An instant, immutable checkpoint of the App + Data + Database is created exactly at the moment of release.
The Safety Net: If the new code corrupts the database, you don't lose 4 hours of data. You perform an Application-Level Rollback to the exact second before the deployment. Your RPO is effectively zero relative to the release.
4. Handling the "New and Unknown"
DevOps moves fast. If a developer decides to implement a new vector database for AI or a new NoSQL store, traditional agent-based backups will fail because they don't "know" this new technology.
The Solution: IssProtect utilizes Blueprint technology. This allows the system to understand and protect new database technologies instantly, without waiting for a vendor update.
Summary: Synchronizing Your Success
To achieve true business resilience, your data protection strategy must be as modern and agile as the applications it protects.
Traditional IT has mastered resilience through heavy investment in near-zero RPO solutions and expensive "Clean Room" concepts.
Modern IT has lagged behind, suffering from an "Asynchronous Nightmare" where code, data, and databases operate on conflicting backup schedules.
IssProtect for DevOps eliminates this chaos by introducing Backup-As-Code. By integrating application-aware, immutable snapshots directly into the CI/CD pipeline, we ensure that your RPO moves at the speed of your releases, not the speed of a legacy scheduler.
A Critical Distinction: It is vital to understand that IssProtect for DevOps is purpose-built for the Kubernetes ecosystem. It is not a tool for protecting legacy Traditional IT (VMware/Hyper-V), keep your existing backup infrastructure for traditional workload, but do not use your traditional tools for modern workload.
However, for organizations seeking a unified future, we can assist in converting your legacy VMs into an OpenShift environment. By running a hybrid solution—mixing VMs and Containers on a single, modern platform like IBM Fusion—you can extend this modern, automated protection to your entire estate.